From Eric Muchell
After the flood disaster, Germany will now also use the “Cell-Broadcast” warning system. This is based on the standardized warning system “EU-Alert”, which will be introduced across the European Union in 2022. So far, Germany has used three different applications, none of which played a role in the flood disaster.
On the other hand, “Cell Broadcasting” has been technically integrated into all cellular networks since the introduction of GSM, and therefore it works without additional software on an old Nokia mobile phone as it does on an iPhone for 5G. Mobile communications developer Harald Welte, who had already extensively tested “Cell Broadcast” in 2014, spoke to ORF.at about the features of this system.

research
This is the latest stable version of ETSI specification for cellular broadcasting From 2019. The first version comes from 2001. The European Telecommunication Standards Institute (ETSI) standardizes all the processes and technical requirements in mobile networks in Europe, the actual work being done under the “Third Generation Partnership Project” (3GPP), part of the “International Consortium Telecom” (ITU) heard. This, in turn, is a subsidiary organization of the United Nations, that is, the United Nations. Note that the abbreviation EMTEL is also used in cellular broadcasting (more on this below).
How does cellular broadcasting work?
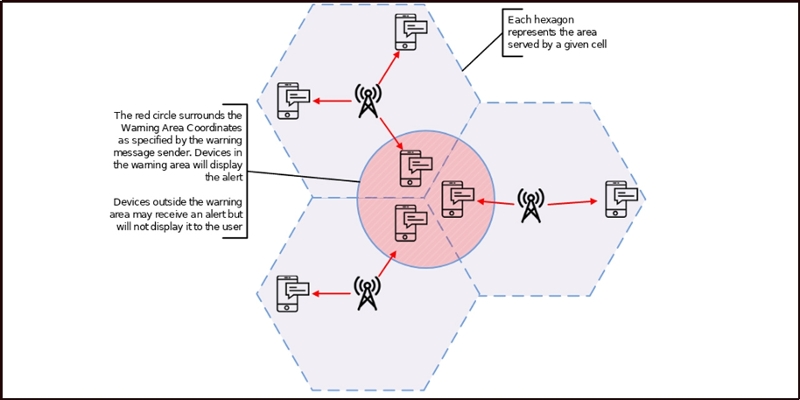
The cellular broadcast message is technically similar to SMS, but it allows texts of up to 1,395 characters to appear on the screen without user interaction, even if the screen is obscured. At the same time, a loud standard alarm will sound and the mobile phone will vibrate. This also works when the cell phone is muted. Unlike SMS, this message is not sent to a terminal device, but to all mobile phones registered with one, several or more specific radio masts. This largely prevents the alarm from appearing on the mobile phones of unaffected users who are not affected by the alarm. So it is a broadcast system like radio or television, but with one difference that can be determined on an ad hoc basis, i.e. a geographically defined “audience” that must be accessed exclusively and not so, in order to avoid panic.
“You don’t need any additional hardware for this. The functions of the most important component, called the Cell Broadcasting Center, are usually available on all base stations, so the operator just has to configure it to be able to use it,” said Harald Welty. The network level is somewhat more complicated because there are a large number of different processes running in each cellular network.” All networks owned by cellular operators are configured completely differently, only the configuration in question should comply with the framework of technical specifications of 3GPP, ETSI and on On a technical level, these networks are only similar to each other, but in no way identical.
Brick
This graph comes from the European Union authority BEREC, in which all national telecom regulatory authorities are represented in the European Union showing a future advanced version of the cellular broadcast system, which includes not only radio cells but also GPS data. This proposal was made by the Netherlands, where Cell Broadcast has been there since 2012 [!] In practical use. BEREC إرشادات Guidelines List some of the most fun shortcuts.
“Technically simple comparison”
“Thus these differences in mobile radio networks do not allow for more accurate calculations of how long this broadcast service will last in a mobile radio network, which is equally valid for all networks. So I can only give a rough estimate that it will take a few months on average. “From a technical point of view, SMSCB is very simple when you compare this service with almost all other components of cellular technology”
SMSCB is just a synonym for cellular broadcasting, in the mobile radio sector two to three commonly used synonyms are not an exception for every important term, but the rule, since standardization takes place in an international context. Therefore, the first step in every standardization process in mobile radio networks is always a list of synonyms already used by the technicians and regulatory authorities involved at the national level. This is how the term “cellular broadcast” came from Europe, but regulators in the European Union use a different name for the same service, which is “ECS-PWS”. This acronym stands for Public Alert System for Electronic Communications Services.

OSMOCOM
Here’s a reasonably high-tech video on how to do Osmocom Free Software System for Professional Use Weltes zu . Blog Free cellular software and severe weather disaster
Cell broadcast im Hackertest
“Apart from technicians’ hours, I don’t really see any major cost factors facing mobile operators. Base station manufacturers may require mobile operators to pay an additional license fee for this feature. It is possible, but I don’t know exactly,” Welte said. I’m a free software developer and certainly have nothing to do with commercial trading in mobile communications.” Since 2009, Welte and a small team of mobile communications hackers build at every conference and every Chaos Computer Club has its own GSM network based on 3GPP and ETSI technical specifications .
These networks run on free software for GSM, which was developed within the same Osmocom project. “We had SMSCB up and running for the first time in 2014 in Congress, but then we haven’t dealt with it for a while. It initially worked and we knew exactly what it would take. In 2019, this first hack was expanded by Cell Broadcast, i.e. “ “Proof of concept”, to a full 2G implementation based on the GSM standard. This was only possible with a grant of 35,000 euros. Unfortunately, this money was not enough to develop 4G and so far no one has been found who wants to fund or promote it. Obviously Exactly to us how it should be done – the standards are technically well defined – it should actually just be implemented. But at the moment there is no money for that.”
Conclusion
The hacker’s implementation of Cell Broadcast in standards organizations ranks on the same level as the commercial programs of Nokia, Ericsson, and all other manufacturers. All 3GPP and ETSI standards are formulated in a completely technology-neutral manner. The only difference will be in the level of security of the programs, because the programs developed by real hackers are usually completely safe because they have just been tested by the hackers. Criminals in any case as well as government agencies must remain abroad, and in this case also for the 19 secret services of the German Federal Republic of Troy.
German politicians have not yet spoken, but the CEO of Telekom has already sent a message through the company’s news portal to implement cellular broadcasting immediately. With the addition: Once a tender has been issued to the German Federal Government.

“Devoted gamer. Webaholic. Infuriatingly humble social media trailblazer. Lifelong internet expert.”





