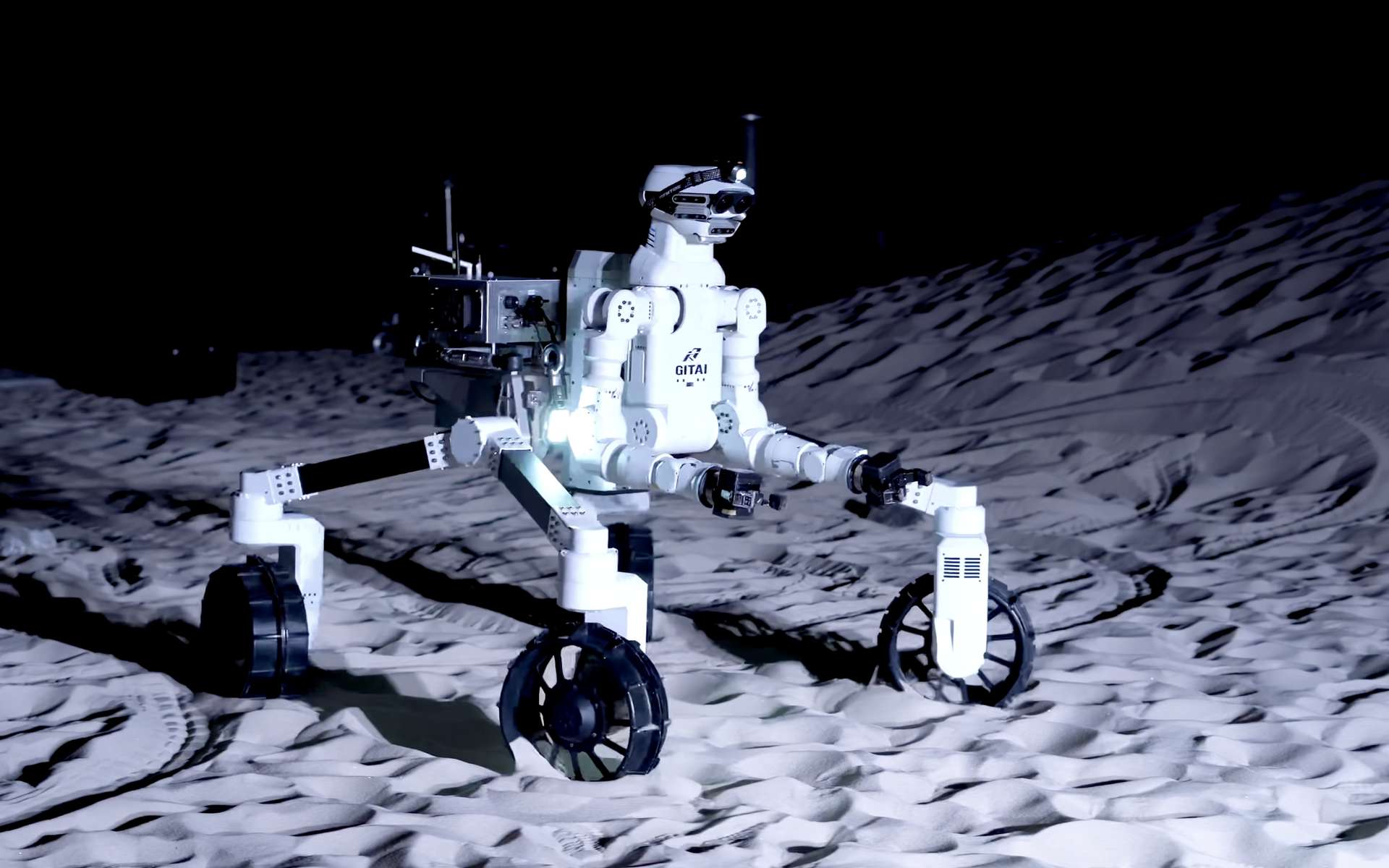
In December 2021, Japanese robotics company Gitai was testing its R1 rover, commissioned by Jaxa and intending to travel to the Moon. A video clip, published a few months later, allows to admire the capabilities of the device in realistic conditions that reproduce the characteristics of the lunar regolith.
In parallel with the Artemis program, some space agencies are preparing for their upcoming arrival on the moon with the rover. It is for Japan Space Agency In partnership with the Japanese company specialized in Robotics, Jitai. In September 2020, Jaxa announced the establishment of cooperation with the private company with the aim of design robots assigned to carry out missions in space.
To this end, Jitai has developed a multifunctional rover, discreetly called the R1. In December 2021, the capabilities of the R1 were tested in real-world conditions, on a surface that simulates a plain on the Moon and its idiosyncrasies. In a video posted in February 2022, the robot wowed with its fluidity and capabilities. Thus, the rover can easily maneuver and change direction, overcoming natural obstacles or even collecting objects on the ground. The experiment was conducted at the Sagamihara campus in Japan.
Technology marvel
The R1 is equipped with four legs whose multi-directional wheels allow the vehicle to quickly adjust its position. Testing has shown that the unit is able to overcome obstacles and medium-sized rocks, with the rover box raised or lowered. Thanks to its mobility, it can also climb slopes whose inclination is estimated between 15 and 20 degrees.
There are two articulated arms at the front of the robot making it possible to carry out scavenging operations on the ground. The two handles positioned at the end of the arms can use a small shovel to drop samples of lunar dust into a container which is then sealed by the rover before being stored in a container. The levers, divided into several parts, give the R1 a wide range of motion. The device is remotely controlled by an engineer, makes precise and technical gestures: he can easily separate a belt from the package, move it and use tools. Jitai showcases her expertise by building her rover relay contact And a set of solar panels. R1 precisely performs the movements required to assemble the structure, by tightening the struts or by adjusting the position of the solar panels.
R1, more efficient than human?
The collaboration created between Jaxa and Gitai aims to democratize robotic missions to space and the moon. L ‘Japan Space Agency He wants to oversee operations at a low financial cost, with robots operating efficiently where humans can’t go. on his site InternetAnd the Japanese company reveals its ambitions: Participation in the construction of the lunar bases and Mars in the early forties and beyond.
Regarding the R1 rover, an impressive technical presentation in December 2021 should confirm the Japanese Aerospace Administration’s ambition for robotic missions to the Moon. Gitai notes in the video presentation of the rover that the rover could quickly make its first turns in lunar dust, as early as 2025.
SPECIAL OFFER: For Father’s Day, give the best of science!
Your dad is great science enthusiast And extraordinary discoveries? And if I offered him a Fantastic science exploration In paper form? benefit from -20% on Mag Futura (Special offer: 15 euros instead of 19 EUR): 220 pages to explore 4 scientific issues that will shape our future!
Mag Futura is:
- 4 key science questions for 2022, from Earth to the Moon
- 220 pages, 60 experts: No fake news, just science
- Home delivery with e-gift card
- independent scientific media
Interested in what you just read?

“Professional food nerd. Internet scholar. Typical bacon buff. Passionate creator.”