Understanding electric vehicles and how they are charged can be a great topic for your next business dinner. Don’t miss out on this article as you’ll find plenty of information to absorb and impress people. To begin, you need to understand the difference between a DC Fast Charger and a Level 2 (AC) charger. “DC” stands for “direct current”, which is the type of power used by vehicle batteries, while “AC” (or “Level 2”) is for “alternating current”.
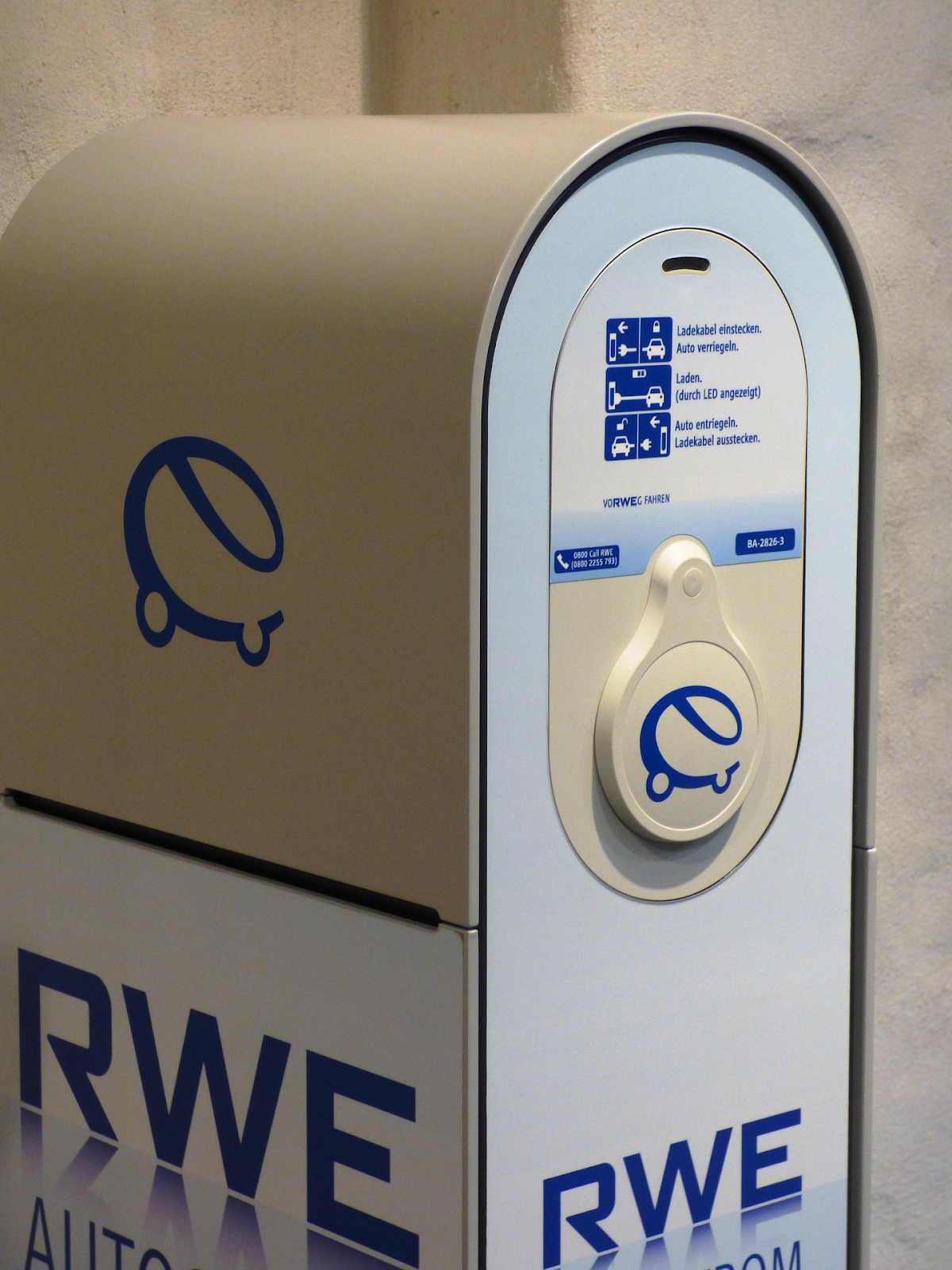
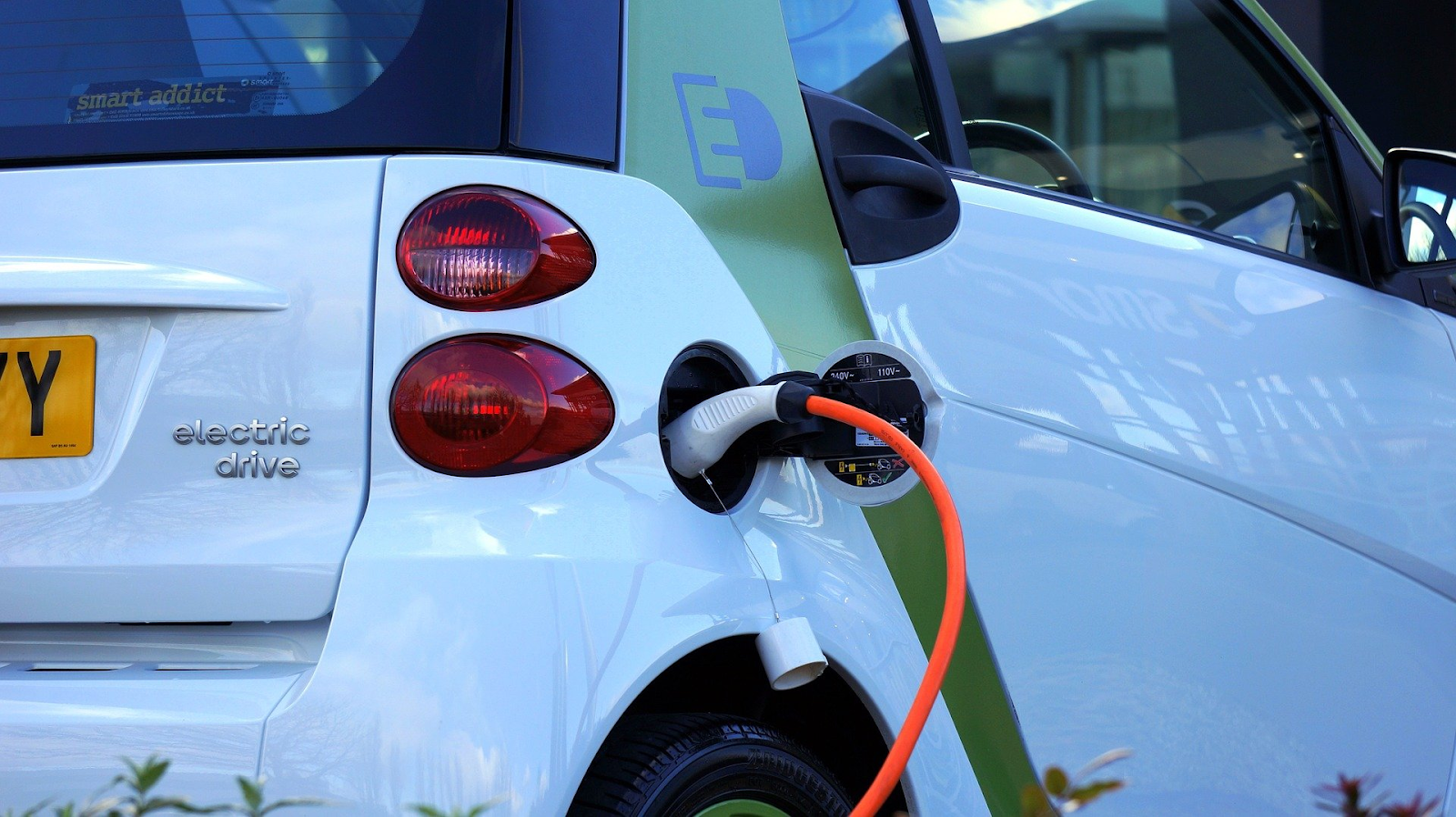
You may be wondering “What are the main differences between a DC Fast Charger, and a Level 2 charger?”. In AC chargers, AC power is supplied from the charging station to the onboard charger, which supplies the DC power to the battery; while DC fast charging stations provide DC power directly to the vehicle’s battery.
An EV Fast Charger has CHAdeMO ports, which is an electric car battery charging protocol that delivers up to 62.5 kW, 500 V, 125 A of high-voltage DC direct current through an electrical connector. A CHAdeMO electric car fast charger can charge an electric vehicle to its 80%, in just 30 minutes.
The future is electric
The pollution caused by the gases emitted by gas-powered cars is an unavoidable fact. The relationship between fuels and the environment is direct, and it has an undeniable impact on it. The mechanical propulsion of regular cars emits three major gases: CO2 (carbon dioxide), NOx (nitrogen oxide), and particulate matter. In general, the cars that emit the fewest gases are the ones that consume the fewest CO2, which are the diesel engines.
The evidence of the damage caused by the emission of the aforementioned gases led the automotive industry to look for a more sustainable alternative, which is how electric cars were born. EVs are a patent reality in several countries, as they are gaining ground in sales compared to cars with combustion engines. Among the advantages of electric vehicles, we can find:
Zero emissions. Cars that are 100% electric and use DC fast charging stations do not emit polluting gases. This is an essential advantage when thinking about the importance of taking care of the environment.
Low maintenance. The maintenance of an electric vehicle is simply reduced to a check every once in a while to examine the state of the batteries and electric motors. No need to use various liquids or change filters.
More relaxed driving. Considering that electric cars do not emit sound, noise pollution is null. This advantage is not only for the person driving the vehicle, but for everyone around. In addition, EVs do not need to shift gears constantly, which translates into a smoother ride.
Where to find an EV fast charger
If you are near Oregon, Washington or California, and you own an EV, you must try driving along West Coast Electric Highway (WCEH). It is an extensive network of 56 EV chargers, including Level 2 and the famous electric car fast chargers. This highway is the result of a public-private initiative, funded in part by the US Departments of Energy and Transportation (DOE and DOT) through the Oregon and Washington State Departments of Transportation.
This means that you will find an electric vehicle charging zone every 25 to 50 miles, along specific routes. These charging stations are usually located in convenient, hassle-free areas, and in areas where there are other activities to do while the electric car is charging, such as restaurants, grocery stores, and shopping malls.
The West Coast Electric Highway is the largest contiguous network of DC fast chargers in the United States, and is also an example to follow for other roads and highways. In this way, we give security to all those drivers of electric vehicles and contribute to the adoption of new sustainable technologies to help take care of our environment.

“Beer practitioner. Pop culture maven. Problem solver. Proud social media geek. Total coffee enthusiast. Hipster-friendly tv fan. Creator.”