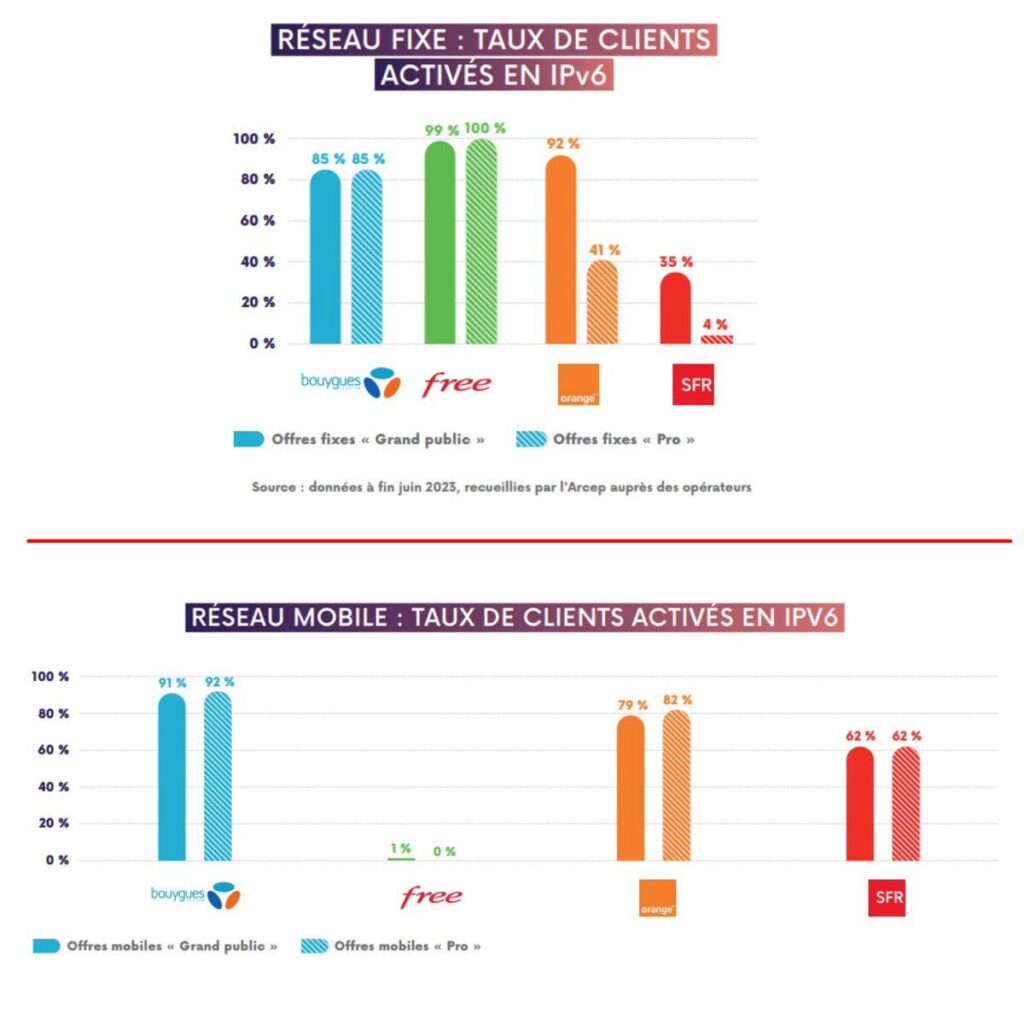
Free, an operator known for its innovations and attractive offers, has made significant progress in deploying IPv6, especially within its professional services (Free Pro) and on its fixed network. However, its mobile network appears to be lagging behind in comparison. However, there are a few possible reasons behind this disparity.
Source: Arib
A matter of needs and priorities above all else.
Businesses, especially those in the technology sector, have specific needs when it comes to connectivity, performance, and security. IPv6 offers better IP address management, which is essential for businesses with complex networks and large numbers of connected devices. So, it’s only natural that Free Pro prioritizes IPv6 deployment to meet these needs.
For individuals, connectivity needs are generally less complex. The majority of users are satisfied with IPv4 for common activities such as web browsing, streaming, and online gaming. Therefore, moving to IPv6 on the mobile network was not an urgent priority for Free, but the brand remains very successful in this area on the fixed network.
IP Address Management: An Absolute Must for Fixed and Professional Networks
The shortage of IPv4 addresses is a growing problem. IPv6, with its nearly infinite number of addresses, represents a long-term solution. This transition is especially important for fixed and professional networks where effective IP address management is essential for the proper operation of services.
On the mobile network, providers can continue to use technologies like Network Address Translation (NAT) to expand the use of IPv4, making an immediate transition to IPv6 less urgent. The transition is therefore less urgent for some operators, which explains this strategy on Free’s part.
Performance and reliability: a priority for fixed networks
IPv6 can improve network performance by reducing some of the bottlenecks associated with IPv4. This improvement is particularly useful for fixed networks where stability and speed are critical for uses such as high-definition streaming, online gaming, and remote work.
On a mobile network, while performance is important, users tolerate differences in connection quality more easily. Additionally, mobile infrastructures are constantly being updated to improve performance even under IPv4.
Security: A major concern for businesses and fixed networks.
IPv6 includes more robust security features than IPv4, such as Internet Protocol Security (IPsec). These features are particularly attractive to businesses that need to protect large amounts of sensitive data.
Although security is also important for mobile users, the risks and requirements are often lower than in business environments. Existing IPv4 security solutions are generally sufficient to meet the needs of mobile users.
The move to IPv6 for fixed and professional networks has been faster because it directly addresses operational and strategic needs. As a result, Free Pro and Free Fixed services have benefited from more aggressive and targeted deployments.
Mass deployment of IPv6 on mobile networks involves significant investment and complex management of existing equipment. The free version must ensure that all mobile devices and network infrastructure are IPv6 compatible, making the transition slower and more expensive.

“Devoted gamer. Webaholic. Infuriatingly humble social media trailblazer. Lifelong internet expert.”





